一、Spring初见
优点
Spring是开源免费的框架(容器)
Spring是轻量级、非入侵式的框架
控制反转(IOC),面向切面编程(AOP)
支持事物的处理,对框架整合的支持
配置
看看
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-webmvc -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.1.17.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.projectlombok/lombok -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.12</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<!--junit-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies><?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="hello" class="com.ming.pojo.Hello">
<property name="name" value="Spring" />
<constructor-arg index="0" value="MINGYUE" />
<constructor-arg name="name" value="MINGYUE" />
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="MINGYUE" />
</bean>
<!-- more bean definitions go here -->
</beans>public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
Hello hello = (Hello) context.getBean("hello");
Hello hello1 = context.getBean("hello", Hello.class);
System.out.println(hello.toString());
}
}
创建对象
1.使用无参构造创建对象,默认!
2.假设我们要使用有参构造创建对象
<bean id="hello" class="com.ming.pojo.Hello" name="otherName1,otherName2">
<property name="name" value="Spring" />
<constructor-arg index="0" value="MINGYUE" />
<constructor-arg name="name" value="MINGYUE" />
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="MINGYUE" />
</bean>在配置文件加载的时候,容器中管理的对象就已经初始化了
别名
<!--别名,如果添加了别名,我们也可以使用别名获取到这个对象-->
<alias name="user alias="userNew"/>import
合并
<import resource="beans.xml"/>
<import resource="beans1.xml" />
<import resource="beans2.xml"/>依赖注入
构造注入
set注入
public class student {
private String name
private Address address;
private String[] books;
private List<String> hobbys;
private Map<String, String> card;
private Set<String> games;
private Properties info;
}<bean id="moreComplexObject" class="example.ComplexObject">
<bean class="ExampleBean">
<property name="email">
<null/>
</property>
</bean>
<!-- results in a setAdminEmails(java.util.Properties) call -->
<property name="adminEmails">
<props>
<prop key="administrator">administrator@example.org</prop>
<prop key="support">support@example.org</prop>
<prop key="development">development@example.org</prop>
</props>
</property>
<!-- results in a setSomeList(java.util.List) call -->
<property name="someList">
<list> <!--Array-->
<value>a list element followed by a reference</value>
<ref bean="myDataSource" />
</list>
</property>
<!-- results in a setSomeMap(java.util.Map) call -->
<property name="someMap">
<map>
<entry key="an entry" value="just some string"/>
<entry key ="a ref" value-ref="myDataSource"/>
</map>
</property>
<!-- results in a setSomeSet(java.util.Set) call -->
<property name="someSet">
<set>
<value>just some string</value>
<ref bean="myDataSource" />
</set>
</property>
</bean>
扩展方式注入
需要导入约束
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:annotation-config/>
<!-- p参数 -->
<bean name="p-namespace" class="com.example.ExampleBean"
p:email="someone@somewhere.com"/>
<!-- traditional declaration with optional argument names -->
<!-- c构造 -->
<bean id="beanOne" class="x.y.ThingOne">
<constructor-arg name="thingTwo" ref="beanTwo"/>
<constructor-arg name="thingThree" ref="beanThree"/>
<constructor-arg name="email" value="something@somewhere.com"/>
</bean>
<!-- c-namespace declaration with argument names -->
<bean id="beanOne" class="x.y.ThingOne" c:thingTwo-ref="beanTwo"
c:thingThree-ref="beanThree" c:email="something@somewhere.com"/>
</beans>作用域
默认singleton scope="singleton"

自动装配
装配方式
- xml显示配置
- java显示配置
- 隐式自动装配
autowire
- byName
- 名称相同
- byType
- 类型全局唯一
<bean id="cat" class="com.kuang.pojo.Cat"/>
<bean id="dog" class="com.kuang.pojo.Dog"/>
<!-- byName:会自动在容器上下文中查找,和自己对象set方法后面的值对应的名称 -->
<bean id="people" class="com.kuang.pojo.People" autowire="byName">
<property name="name" value="明月"/>
</bean>注解装配
使用
属性上@Autowired
使用后不用编写set方法(反射),但是这个属性需要在IOC容器中存在,且符合byType获取,如果不能唯一确定,则需要使用@Qualifier
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:annotation-config/>
</beans>@Autowired
@Nullable 标记这个字段可以为null
@Qualifier(value="指定id")
@Resource
@Resource(name = "cat1")
先通过name获取,再通过type获取注解开发
注册
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 指定包下的注解生效 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.ming.pojo"/>
<context:annotation-config />
<!-- 类上添加@Component,即可注册 -->
</beans>Bean
类上添加@Component,即可注册
@Scope("singleton")
属性注入
属性或者set方法上添加注解
@Value("ming")
component衍生
dao @Repository
service @Service
controller @Controller
对比
xml:万能、维护方便
注解:只能使用自己的类,不易于维护
一般
xml用来管理bean
注解只负责完成属性的注入
注解生效,需要开启注解的支持
<context:component-scan base-package="com.ming.pojo" /> <context:annotation-config />
使用java的方式
我们现在要完全不使用 Spring的xm配置了,全权交给java来做
// config/MingConfig
@Configuration // 类似xml注册bean
@ComponentScan("com.ming.pojo") // 扫描注册包下有@component注解的类
// @Import(sha.class)
public class MingConfig {
@Bean // 只使用这个也能注册
public User user() {
return new User();
}
}
// User
@Component
public class User {
public String name = "ming";
}
// Test
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MingConfig.class);
User user = applicationContext.getBean("user", User.class);
System.out.println(user.name);
}代理模式
SpringAop的底层
代理模式分类
- 静态代理
- 动态代理
静态代理
角色分析
- 抽象角色:一般会使用接口或者抽象类来解决
- 真实角色:被代理的角色
- 代理角色:代理真实角色,代理真实角色后,我们一般会做一些附属操作(很多功能)
- 客户:访问代理的人
好处
- 真实角色的操作更纯粹,不去关注公共的业务
- 公共交给了代理角色,实现业务的分工
- 公共业务发生扩展的时候,方便集中管理
缺点
- 一个真实角色产生一个代理角色,代码增加,开发效率低
横切,便于扩展
动态代理
代理类是动态生成的,不是直接写好的
分类
- 基于接口 – JDK动态代理
- 基于类 –cglib
- java字节码 –javassist
好处
- 真实角色的操作更纯粹,不去关注公共的业务
- 公共交给了代理角色,实现业务的分工
- 公共业务发生扩展的时候,方便集中管理
- 一个动态代理类代理的是一个接口,一般对应一类业务
- 可以代理多个实现同一接口的类
Proxy、InvocationHandler
package com.ming.demo02;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
// 自动生成代理类
public class ProxyInvocationHandler implements InvocationHandler {
// 被代理的接口
private Object target;
public void setTarget(Object target) {
this.target = target;
}
// 生成得到代理类
public Object getProxy() { // 类在哪个位置 接口 InvocationHandler
return Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.getClass().getClassLoader(), target.getClass().getInterfaces(), this);
}
// 处理代理实例,并返回结果
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
log(method.getName());
// 动态代理的本质,使用反射实现
Object result = method.invoke(target, args);
return result;
}
public void log(String msg) {
System.out.println("[INFO]"+msg);
}
}
使用
public static void main(String[] args) {
UserServiceImpl userService = new UserServiceImpl();
ProxyInvocationHandler pih = new ProxyInvocationHandler();
pih.setTarget(userService);
UserService proxy = (UserService) pih.getProxy();
proxy.add();
proxy.delete();
}AOP
依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.4</version>
</dependency>使用spring接口
第一种 给他用啥
给该切面使用方法前和方法后
applicationContext.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!-- 注册bean -->
<bean id="userService" class="com.ming.service.UserServiceImpl" />
<bean id="afterLog" class="com.ming.log.AfterLog" />
<bean id="log" class="com.ming.log.Log" />
<!-- 使用原生aop -->
<!-- 配置aop -->
<aop:config>
<!-- 切入点 expression(要执行的位置) -->
<aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* com.ming.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))" />
<!-- 执行环绕 -->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="log" pointcut-ref="pointcut" />
<aop:advisor advice-ref="afterLog" pointcut-ref="pointcut" />
</aop:config>
</beans>log
package com.ming.log;
import org.springframework.aop.MethodBeforeAdvice;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Log implements MethodBeforeAdvice {
public void before(Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
System.out.println(target.getClass().getName() +"的" +method.getName() +"方法被执行了");
}
}public class AfterLog implements AfterReturningAdvice {
public void afterReturning(Object returnValue, Method method, Object[] args, Object target) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("执行了" +method.getName() +"方法,返回结果为" +returnValue);
}
}
Test
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
//UserService userService = (UserService) applicationContext.getBean("userService");
UserService userService = applicationContext.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
userService.add();
}
}
第二种 将它给谁
定义切面,定义该切面的方法前后
<bean id="diy" class="com.ming.log.Diy" />
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect id="diy" ref="diy">
<aop:pointcut id="pointcut1" expression="execution(* com.ming.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))" />
<aop:after method="after1" pointcut-ref="pointcut1" />
<aop:before method="before1" pointcut-ref="pointcut1" />
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>第三种
<bean id="annotationPointCut" class="com.ming.log.AnnotationPointCut"/>
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/> <!-- 注解支持 -->package com.ming.log;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import javax.xml.ws.Action;
@Aspect /// 声明
public class AnnotationPointCut {
@After("execution(* com.ming.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void after() {
System.out.println("after2");
}
@Before("execution(* com.ming.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void before() {
System.out.println("before2");
}
@Around("execution(* com.ming.service.UserServiceImpl.*(..))")
public void arround(ProceedingJoinPoint jp) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("前");
Object proceed = jp.proceed();
System.out.println("后");
}
}
JDBC
初始化
引入相关 jar 包,在 spring 配置文件配置数据库连接池
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource"
destroy-method="close">
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///test" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="root" />
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
</bean>配置 JdbcTemplate 对象,注入 DataSource
<!-- JdbcTemplate 对象 -->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<!--注入 dataSource-->
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property><!--set方式注入-->
</bean>
<!-- 组件扫描 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu"></context:component-scan>使用
// ---------------- update ---------------------
String sql = "update t_book set username=?,ustatus=? where user_id=?";
Object[] args = {
book.getUsername(),
book.getUstatus(),
book.getUserId()
};
int update = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, args);
// ---------------- delete ---------------------
String sql = "delete from t_book where user_id = ?";
int update = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, id);
// ---------------- select ---------------------
// 查询表记录数
String sql = "select count(*) from t_book";
// queryForObject方法中:第一个参数代表--sql语句;第二个参数代表--返回类型class
Integer count = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, Integer.class);
// 查询一个
String sql = "select * from t_book where user_id=?";
/*
queryForObject方法中:
第一个参数:sql语句
第二个参数:RowMapper 是接口,针对返回不同类型数据,使用这个接口里面 实现类 完成数据封装
第三个参数:sql 语句值
*/
Book book = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(
sql,
new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Book>(Book.class),
id
);
// 查询集合
String sql = "select * from t_book";
//调用方法
List<Book> bookList = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Book>(Book.class));批量操作
List<Object[]> batchArgs = new ArrayList<>();
Object[] o1 = {"3","java","a"};
Object[] o2 = {"4","c++","b"};
Object[] o3 = {"5","MySQL","c"};
batchArgs.add(o1);
batchArgs.add(o2);
batchArgs.add(o3);
// 批量插入
String sql = "insert into t_book values(?,?,?)";
// batchUpdate方法 第一个参数:sql语句 第二个参数:List集合,添加多条记录数据
int[] ints = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, batchArgs);
// 批量更新
String sql = "update t_book set username=?,ustatus=? where user_id=?";
int[] ints = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, batchArgs);
二、整合mybatis
回忆mybatis
mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<!--configuration核心配置文件-->
<configuration>
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.ming.pojo" />
</typeAliases>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useSSL=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8"/>
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</dataSource>
</environment>
</environments>
<mappers>
<mapper class="com.ming.mapper.UserMapper" />
<!--<mapper resource="com/ming/mapper/UserMapper.xml" />-->
</mappers>
</configuration>mapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--configuration核心配置文件-->
<mapper namespace="com.ming.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="getAllUsers" resultType="com.ming.pojo.User">
select * from mybatis.user
</select>
</mapper>test
public void testMybatis01() throws IOException {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
List<User> users = mapper.getAllUsers();
for (User user : users) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}pom导出xml
<build>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>mybatis-spring
初见
http://mybatis.org/spring/zh/getting-started.html
步骤:
spring-dao.xml
- dataSource 准备数据源
- 准备sqlSessionFactory,注入dataSource,绑定mybatis配置文件,注册各个mapper.xml
- 使用sqlSessionFactory构造生成sqlSession(Template)对象
- 使用sqlSession注入对应的接口实现类MapperImpl
- MapperImpl中对应方法使用sqlSession生成mapper对象,返回mapper对象调用方法的结果
导入
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>2.0.5</version>
</dependency><?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<parent>
<artifactId>spring-study</artifactId>
<groupId>com.ming</groupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</parent>
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<artifactId>spring-06-mybatis</artifactId>
<!--导入依赖-->
<dependencies>
<!--mysql驱动-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.47</version>
</dependency>
<!--mybatis-->
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis/mybatis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.10</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>2.0.5</version>
</dependency>
<!--spring操作数据库-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.1.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.1.17.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.4</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<!--在build中配置resources,来防止我们资源导出失败的问题-->
<build>
<resources>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/resources</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
<resource>
<directory>src/main/java</directory>
<includes>
<include>**/*.properties</include>
<include>**/*.xml</include>
</includes>
<filtering>true</filtering>
</resource>
</resources>
</build>
</project>mybatis-config.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<!--configuration核心配置文件-->
<configuration>
<typeAliases>
<package name="com.ming.pojo" />
</typeAliases>
</configuration>spring-dao.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useSSL=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8" />
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</bean>
<!-- SqlSessionFactory -->
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
<!-- 绑定mybatis配置文件 -->
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis-config.xml"/>
<!-- 登记mapper -->
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:com/ming/mapper/*.xml"/>
</bean>
<!-- sqlSessionTemplate就是sqlSession-->
<bean id="sqlSession" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate">
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>
<bean id="userMapper" class="com.ming.mapper.UserMapperImpl">
<property name="sqlSession" ref="sqlSession" />
</bean>
<!-- 可以将其他的mapper抽离到applicationContext使用import导入 -->
</beans>UserMapperImpl
package com.ming.mapper;
import com.ming.pojo.User;
import org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate;
import java.util.List;
public class UserMapperImpl implements UserMapper {
private SqlSessionTemplate sqlSession;
public void setSqlSession(SqlSessionTemplate sqlSession) {
this.sqlSession = sqlSession;
}
public List<User> getAllUsers() {
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
return mapper.getAllUsers();
}
}简化
实现类
public class UserMapperImpl1 extends SqlSessionDaoSupport implements UserMapper {
public List<User> getAllUsers() {
return getSqlSession().getMapper(UserMapper.class).getAllUsers();
}
}注入
只需注入sqlSessionFactory,SqlSessionDaoSupport需要,原本还需要注入sqlSessionTemplate
<bean id="userMapper1" class="com.ming.mapper.UserMapperImpl1">
<property name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory" />
</bean>声明式事务
要么都成功,要么都失败
ACID: 原子性、一致性、隔离性、持久性
隔离性:多个业务处理同一个资源,防止数据损坏;
持久性:事务一旦提交,结果不会被影响
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx
https://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop
https://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache http://www.springframework.org/schema/cache/spring-cache.xsd">
<!--about mysql-->
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useSSL=true&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8" />
<property name="username" value="root"/>
<property name="password" value="root"/>
</bean>
<!-- SqlSessionFactory -->
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
<!-- 绑定mybatis配置文件 -->
<property name="configLocation" value="classpath:mybatis-config.xml"/>
<!-- 登记mapper -->
<property name="mapperLocations" value="classpath:com/ming/mapper/*.xml"/>
</bean>
<!-- sqlSessionTemplate就是sqlSession-->
<bean id="sqlSession" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate">
<constructor-arg index="0" ref="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>
<!--<bean id="userMapper" class="com.ming.mapper.UserMapperImpl">-->
<!--<property name="sqlSession" ref="sqlSession" />-->
<!--</bean>-->
<!-- 事务 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource" />
</bean>
<tx:advice id="txAdvice" transaction-manager="transactionManager">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="*" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!--进行事务切入-->
<aop:config>
<aop:pointcut id="txPointCut" expression="execution(* com.ming.mapper.*.*(..))" />
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="txPointCut"/><!--对哪里使用事务-->
</aop:config>
</beans>三、Spring5
Webflux
https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/reference/html/web-reactive.html
用于Web开发,功能与SpringMVC类似,使用响应式编程
传统Web框架,SpringMVC,这些基于Servlet容器,Webflux是一种异步非阻塞的框架,在Servlet3.1后才支持,,基于Reactor API 实现
异步非阻塞:
异步和同步:针对调用者,调用者发送请求,是否等待回应再去做其他事情
阻塞和非阻塞:针对被调用者,收到请求是否马上反馈
等公交车时我能做其他事情(异步),公交车被调用,公交车广播告诉我,三分钟后进站(非阻塞),没有广播一直等(阻塞)
特点:
- 异步非阻塞:有效资源下提高吞吐量
- 函数式编程:spring5基于java8,使用函数式编程实现路由请求
对比
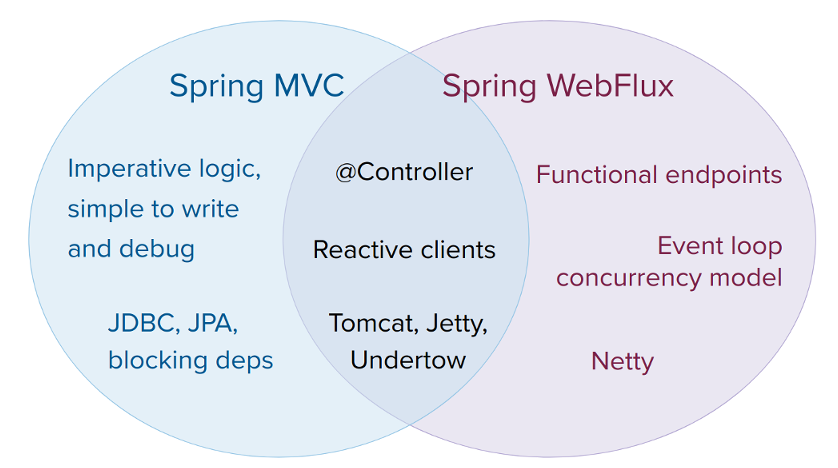
都可以运行到tomcat、注解
springMVC采用命令式编程(一行一行),Webflux采用异步响应式编程
Webflux适用于网关,远程调用
响应式编程:excel中,和是由多个格子决定的,一个格改变,和就改变,观察者模式
java8提供了Observer和Observable
reactor两个核心类:Mono和Flux,实现了Publisher,提供丰富操作符,Flux对象实现发布者,返回N个元素,Mono返回0或者1个元素
flux和mono都是数据流的发布者,都可以发出3种数据信号:元素值、错误信号、完成信号(错误和完成都代表终止,结束数据流)
依赖
<spring-boot.version>2.2.1.RELEASE</spring-boot.version>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.projectreactor</groupId>
<artifactId>reactor-core</artifactId>
<version>3.1.5.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>API
// 声明数据流
Flux.just(1,2,3);
Mono.just(1);
Flux.fromArray(array);
Flux.fromIterable(list);
Flux.fromStream(stream);
// .subscribe(System.out:println) 只有订阅后才会触发数据流
操作符
对数据流操作
map:元素映射为新元素
flatMap:元素映射为流,元素转为流,流合并
执行流程
webFlux基于Reactor,默认容器是netty,netty是高性能NIO框架,异步非阻塞框架
Netty:多路复用,一个选择器
webflux和springMVC流程相似,核心控制器DispatchHandler,实现接口WebHandler
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webflux</artifactId>
</dependency>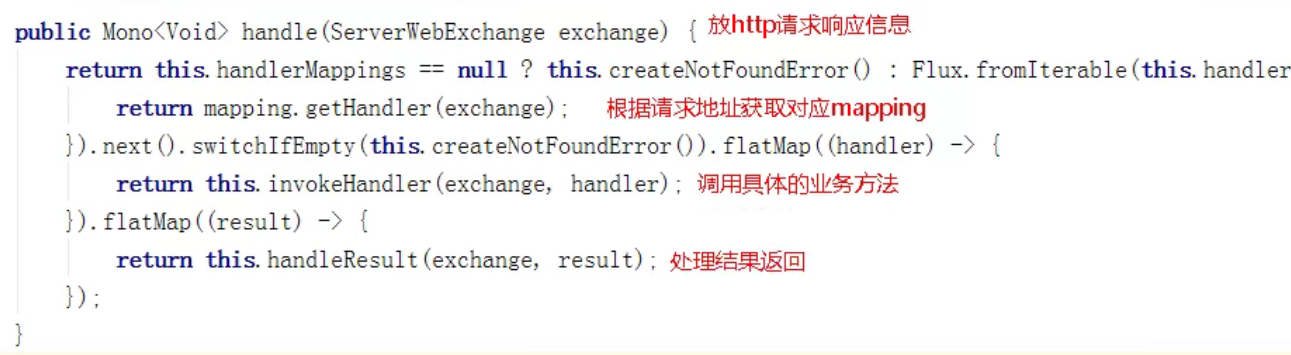
HandlerMapping:根据路径查询方法
HandlerAdaper:适配器,真正负责请求处理
HandlerResultHandler:响应处理结果
SpringWebFlux实现函数式编程,两个接口:RouterFunction(路由功能),HandlerFuction(处理具体函数)
注解使用
与SpringMVC相似,配置相关依赖,SpringBoot自动配置相关运行容器,默认使用Netty服务器
- 创建SpringBoot工程,引入WebFlux依赖
- server.port=8081
- 创建包,controller、service、entity
// new HashMap();
Mono<User> getUserById(int id); // Mono.justOrEmpty(this.users.get(id));
Flux<User> getAllUser(); // Flux.fromInterable(this.users.values());
public Flux<Void> addUser(Mono<User> userMono) {
return userMono.doOnNext(person -> {
user.put(1, user);
}).thenEmpty(Mono.empty());
}SpringMVC同步阻塞,SpringMVC+Servlet+Tomcat
SpringWebFlux,异步非阻塞,SpringWebF+Reactor+Netty
函数式编程使用
1.需要自己初始化服务器,RouterFunction(路由功能,转发给对应Handler)、HandlerFunction(处理请求生成响应的函数)
2.定义函数式接口的实现并且启动需要的服务器
3.SpringWebFlux的请求和响应不再是ServletRequest和ServletResponse,而是ServerRequest和ServerResponse
1.pom依赖
2.实现接口
public Mono<ServerResponse> getUserById(ServerRequest request) {
int userId = Integer.valueOf( request.pathVarible("id") );
// 空值处理
Mono<ServerResponse> notFound = ServerResponse.notFoun().build();
Mono<User> userMono = this.userService.getUserById(userId);
userMono.flatMap(user - > {
ServerReponse.ok().contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.body(fromObject(user))
.switchIfEmpty(notFound);
});
}
public Mono<ServerResponse> getAllUsers(ServerRequest request) {
Flux<User> users = this.userService.getAllUser();
return ServerResponse.ok().contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON).body(user, User.class);
}
public Mono<ServerResponse> saveUser(ServerRequest request) {
Mono<User> userMono = request.bodyToMono(User.class);
return ServerResponse.ok().build( this.userService.saveUserInfo(userMono) );
}初始化服务器,编写Router
public class Server{
public RouterFunction<ServerResponse> routingFunction() {
UserService userService = new UserServiceImpl();
UserHandler handler = new UserHander(userService);
return RouterFunctions.route(
GET("/users/{id}").and(accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)), handler::getUserById)) // org.springframework.web.reactive.function.server.RequestPredicates.GET / access
.andRoute( GET("/users")).and(accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)), handler::getAllUsers);
}
}创建服务器完成适配
public void createRectorServer() {
// 路由和handler适配
RouterFunction<ServerResponse> route = routingFunction();
HttpHandler httpHandler = toHttpHandler(route);
ReactorHttpHandlerAdapter adapter = new ReactorHttpHandlerAdapter(httpHandler);
// 创建服务器
HttpServer httpServer = HttperServer.create();
httpServer.handler(adapter).bindNow();
}使用
// Server
public static void main(String[] args) {
Server server = new Server();
server.createReactorServer();
System.out.println("enter to exit")
System.in.read(); // 退出
}webclient
psvm() {
// 调用服务器地址
WebClient webclient = WebClient.create("http://127.0.0.1:5794");
String id = "1";
User userResult = webClient.get()
.uri("/users/{id}", id) // /users
.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.retrieve()
.bodyToMono(User.class) // bodyToFlux(User.class)
.block();
sout(userResult);
Flux<User> usersResult = webClient.get()
.uri("/users") //
.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.retrieve()
.bodyToFlux(User.class)
.block();
usersResult.map(user - > user.getName())
.buffer().doOnNext(System.out::println).blockFirst();
}注解
AliasFor【TODO】
注解到自定义注解的两个属性上,表示这两个互为别名,简化编码
设置互相别名的属性值必须相同,若两设置成不同,则会报错
定义
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Documented
public @interface AliasFor {
@AliasFor("attribute")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor("value")
String attribute() default "";
/**
* 如果显式设置了AliasFor#annotation()属性
* 并且当前注解中有多个属性指向元注解中的某个属性(可以是直接指向或者通过传递指向),
* 那么这几个属性互为隐式别名
*/
Class<? extends Annotation> annotation() default Annotation.class;
}使用
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Component
public @interface Executor {
@AliasFor("name")
String value() default "";
@AliasFor("value")
String name() default "";
}
关联其他
/**
* 自定义注解MyComponent的value和beanName互为隐式别名,
* 因为它们都指向元注解Component的value属性
*/
@Component
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyComponent {
@AliasFor(annotation = Component.class)
String value() default "";
@AliasFor(attribute = "value", annotation = Component.class)
String beanName() default "";
}